The Public Health Accreditation Board (PHAB) accreditation process is a rigorous assessment of a health department’s capacity to serve its community effectively. By achieving PHAB accreditation, health departments demonstrate their commitment to high-quality performance standards and continuous improvement. One of the key aspects of the accreditation process is the evaluation of the health department’s ability to collaborate with community partners and efficiently manage these relationships.
In this article, we’ll explore how Social Network Analysis (SNA) and relationship mapping can significantly benefit local health departments seeking PHAB accreditation. These powerful tools can help health departments visualize their community partnerships, streamline their collaboration processes, and ultimately improve public health outcomes. Additionally, we’ll introduce PARTNER CPRM as the premier solution in this space, equipped with advanced relationship mapping and visualization features to drive your health department’s success.
Table of Contents
The Power of Relationship Mapping for PHAB Accreditation
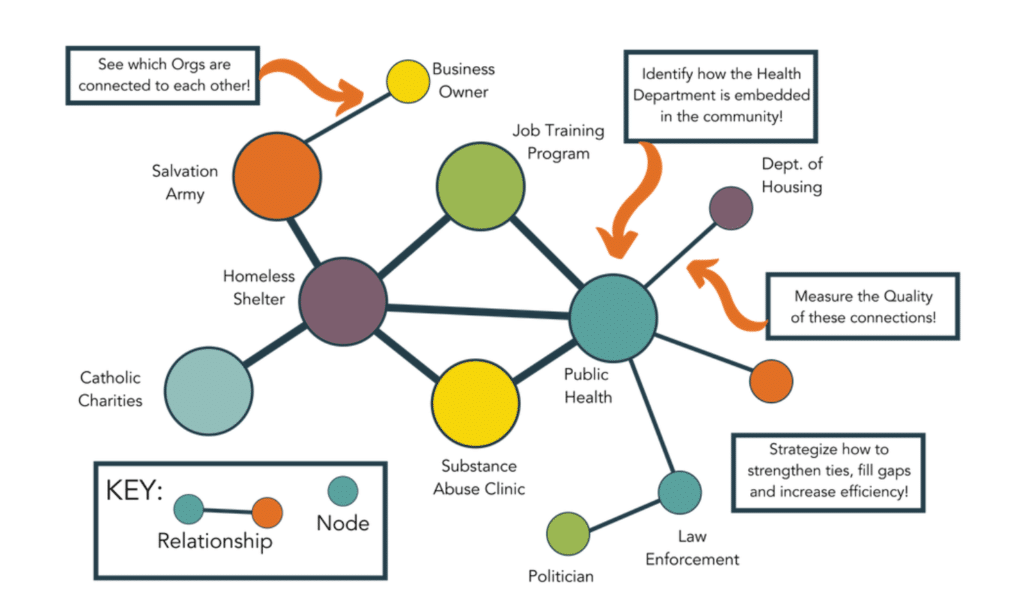
Relationship mapping, a key component of SNA, provides a visual representation of a health department’s community partnerships. By using relationship mapping, health departments can better understand the complex web of relationships that exist within their community, identify areas for improvement, and develop targeted strategies to enhance collaboration and communication. This not only facilitates data-driven decision-making but also helps health departments address the PHAB accreditation requirements related to community engagement, collaboration, and partnership management.
How SNA and Relationship Mapping Support PHAB Accreditation
SNA and relationship mapping can greatly assist local health departments in meeting various PHAB accreditation requirements. Here’s how these tools can support specific domains and standards:
Domain 1 - Assess and monitor population health status, factors influencing health, and community needs and assets:
Social Network Analysis (SNA) and relationship mapping can be invaluable tools for health departments as they work to assess and monitor population health. By visualizing and analyzing the connections between various community organizations, stakeholders, and resources, SNA and relationship mapping enable health departments to identify key partners for collaboration in the community health assessment (CHA) process. This comprehensive and collaborative approach helps ensure that the CHA accurately reflects the needs, assets, and priorities of the entire community.
In addition to identifying partners for data collection, relationship mapping can also be used to identify assets and resources within the community that can be mobilized to address the identified health challenges. For example, the health department may discover through relationship mapping that a local non-profit organization has a successful after-school program that promotes physical activity and healthy eating. The health department could then collaborate with this organization to expand the program’s reach and further address the issue of childhood obesity in the community.
Domain 2 - Investigate, diagnose, and address health problems and hazards affecting the population:
Utilizing relationship mapping and visualization of their network of partners, health departments can enhance their coordination and collaboration efforts in surveillance and investigation. This improved connectivity facilitates more effective communication and data sharing with partner organizations, leading to faster identification and response to health problems and hazards affecting the community.
For example, during a local outbreak of a foodborne illness, a health department could use their relationship mapping and visualization to quickly identify and engage with key partners, such as hospitals, laboratories, and food safety agencies. By leveraging these established connections, the health department can rapidly gather data on reported cases, trace the source of the outbreak, and coordinate efforts to contain it.
Domain 3 - Communicate effectively to inform and educate people about health, factors that influence it, and how to improve it:
Relationship mapping provides health departments with valuable insights into the connections and interactions within their community, enabling them to target communication efforts more effectively. By understanding the key stakeholders and audiences, health departments can tailor their messaging to address specific concerns and needs, fostering a more informed and engaged population.
For example, during a seasonal flu vaccination campaign, a health department could use relationship mapping to identify influential community organizations, such as schools, workplaces, and faith-based groups. By partnering with these organizations, the health department can disseminate tailored, unified messages about the importance of flu vaccination to different audience segments, thereby increasing awareness and vaccination rates. In this scenario, relationship mapping not only assists the health department in meeting Domain 3 requirements for PHAB accreditation but also enhances their ability to educate and inform the community about critical health issues, ultimately contributing to better public health outcomes.
Domain 4 - Strengthen, support, and mobilize communities and partnerships to improve health:
Social Network Analysis (SNA) offers health departments a powerful tool to assess their community partnerships and identify areas for improvement. By visualizing and analyzing their network of connections, health departments can pinpoint gaps in their partnerships and develop strategies to engage new partners or strengthen existing relationships. Metrics such as trust, power, reliability, and centrality can help health departments identify the most effective partners to collaborate with depending on their specific needs, as well as leverage the broader networks of each partner for maximum impact.
For instance, a local health department working to address childhood obesity might use SNA to evaluate their current partnerships with schools, community organizations, and healthcare providers. Through this analysis, they could discover a lack of collaboration with local sports and recreational organizations, which are crucial in promoting physical activity among children. In response, the health department could establish new partnerships with these organizations to implement programs and initiatives designed to increase physical activity and combat childhood obesity.
Domain 9 - Improve and innovate public health functions through ongoing evaluation, research, and continuous quality improvement:
SNA and relationship mapping can provide valuable data and insights that help health departments evaluate their partnership management processes and identify areas for improvement.
Consider a local health department working to improve access to mental health services in their community. By employing SNA and relationship mapping, they can visualize and analyze their existing network of mental health service providers, community organizations, and other stakeholders. This analysis could reveal that while they have a strong network of providers, there is limited collaboration among these partners, leading to fragmented services and less effective care for community members. In response, the health department could facilitate regular meetings or workshops to foster communication and collaboration among partners, as well as establish shared goals and performance metrics. Over time, the health department can use SNA to track changes in the network and measure the impact of their efforts to improve partnership management, ultimately enhancing the quality of mental health services in their community and meeting the requirements for Domain 9 of PHAB accreditation.
Introducing PARTNER CPRM: The Premier Solution for Community Partner Relationship Management
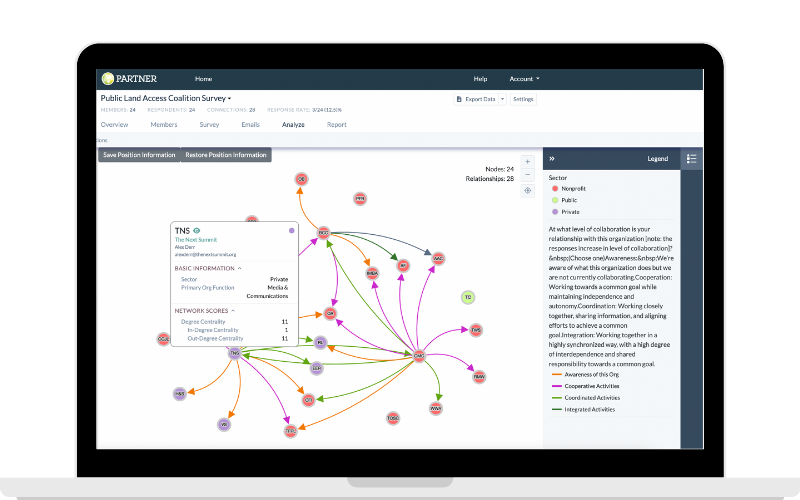
Take the first step towards a more collaborative and data-driven approach to public health by leveraging PARTNER CPRM’s advanced relationship mapping and visualization features. With PARTNER CPRM, your health department will be better equipped to meet PHAB accreditation requirements and foster strong, sustainable partnerships that contribute to the health and well-being of your community.
Request a Demo of PARTNER CPRM.
Take advantage of the opportunity to transform your health department’s community collaboration and partnership management efforts. Request a demo of PARTNER CPRM today and discover how our cutting-edge solution can help you visualize and analyze your community partnerships, enhance your collaboration processes, and successfully achieve PHAB accreditation.
PHAB Accredidation: The Last Word
Social Network Analysis and relationship mapping are powerful tools that can significantly enhance local health departments’ ability to meet PHAB accreditation requirements related to community engagement, collaboration, and partnership management. By employing these methods, health departments can optimize their resources, make data-driven decisions, and ultimately improve public health outcomes for their communities. PARTNER CPRM is the premier solution in this space, offering advanced relationship mapping and visualization features to support your health department’s journey towards PHAB accreditation. Request a demo today and unlock the full potential of your community partnerships.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A: PHAB (Public Health Accreditation Board) accreditation is a voluntary process that assesses the performance of local and state health departments against a set of nationally recognized, practice-focused standards. Achieving PHAB accreditation demonstrates a health department’s commitment to quality improvement, accountability, and the highest levels of performance in serving its community. Accreditation can lead to improved public health outcomes, increased credibility, and enhanced collaboration with community partners.
A: SNA and relationship mapping are valuable tools for visualizing and analyzing the complex network of partnerships and collaborations that health departments engage in to address public health challenges. By using these tools, health departments can better understand the strengths and gaps in their partnerships, optimize resource allocation, and make data-driven decisions that align with PHAB accreditation requirements related to community engagement, collaboration, and partnership management.
A: PARTNER CPRM is a comprehensive solution that simplifies the management, tracking, and visualization of community partnerships. With its advanced relationship mapping and visualization features, PARTNER CPRM can help health departments meet various PHAB accreditation requirements by providing insights into the effectiveness of their collaborations, identifying areas for improvement, and facilitating data sharing among partners. This ultimately leads to more efficient and impactful public health initiatives that align with PHAB standards.
A: Yes, PARTNER CPRM can be particularly helpful for meeting PHAB requirements related to domains such as assessing and monitoring population health (Domain 1), strengthening and mobilizing communities and partnerships (Domain 4), and improving public health functions through ongoing evaluation and research (Domain 9). By leveraging PARTNER CPRM’s tools and insights, health departments can more effectively demonstrate their compliance with PHAB standards and their commitment to improving public health outcomes.